Retirement, Health Care and Disability
Superannuation Key Summary
- Total Superannuation Assets:
- $3.9 trillion at the end of the March 2024 quarter
- Employer Contributions:
- $133.3 billion for the year ending March 2024, 12.4% increase compared to the previous year
- Influenced by Super Guarantee (SG) rate increase to 11% from 1 July 2023, employment growth, and higher wage inflation
- Member Contributions:
- $43.7 billion for the year ending March 2024, 8.2% increase compared to the previous year
- Rate of Return:
- 4.9% for the March 2024 quarter
- 10.9% for the year ending March 2024
- Five-year average annualised ROR: 6.4%
Retirement and Social Security
Retirement and Social Security
- Insurance provides financial security in the event of death, injury, or damage to property.
- Major risks: longevity risk, health deterioration, unemployment.
- Social security benefits: income for retirement, unemployment, and other benefits.
- Financing: taxation system, specific levies, or overall tax revenue.
Example 10.1: How are health costs financed in Australia?
- Medicare provides coverage for hospital and medical treatment.
- Financing: partly from a direct Medicare levy, mostly from taxation revenue.
Longevity Risk and Dependency Ratio
- Longevity risk: individuals live longer than average, requiring more resources post-retirement.
- Dependency ratio: increasing due to improved mortality and lower fertility rates.
- Example: OECD countries’ dependency ratios expected to increase by 40% over the next 40 years.
Retirement Income and Superannuation
Retirement Income Arrangements
Types of retirement income arrangements:
- By provider: Publicly or Privately provided
- Publicly provided: Government provided benefits, funded from general revenue or social security taxes (generally publicly managed)
- Publicly mandated: Government regulation requires compulsory private provision (generally privately managed)
- By funding method: PAYG (pay-as-you-go) or Funded
- PAYG: Benefits are paid out of current income (e.g. government general revenue or specific social security or payroll taxes, firms’ profits)
- Funded: Accumulation of assets to provide for future liabilities
- By benefit design: DB (defined benefit) or DC (defined contribution)
Retirement Income in Australia
Australia’s ‘three-pillar’ approach:
- Public Age Pension
- Compulsory Superannuation (Superannuation Guarantee)
- Voluntary Retirement Savings (Superannuation and other)
Publicly provided PAYG pension
- Eligibility:
- Qualifying age: 67
- Residence requirements: Australian resident for 10 years
- Means-tested: Subject to income and assets tests
- Coverage:
- Around 75% of people of Age Pension eligibility age receive Age Pension.
- Benefits:
- Payments indexed 6 monthly.
- Subject to income and assets tests.
- Full pension rates (2024): $26,535.6 (single)
- The full Age Pension allows only a modest lifestyle for retiree homeowners in good health!
Superannuation
Publicly mandated privately managed occupational pension system (predominantly DC)
- Mandatory employer contribution - 11.5% of an employee’s earnings (set to increase to 12%)
- Preserved benefits - generally superannuation can only be accessed when you reach a specific age (60)
- Concessionally taxed - concessional taxation of contributions fund income (earnings) and benefits
- Tax-free benefit payments for over 60
- Final benefits depend on various factors such as contributions, investment returns, fees, etc.
Defined Benefit Funds
Feature: Retirement benefit is defined (by a pre-determined formula based on factors e.g. years of service, salary etc.)
Example 10.4: Main form of retirement benefit from a DB fund.
- A common benefit for a superannuation fund paying a defined benefit would be a pension of:
where ( n ) is the number of years of membership of the fund and FAS is the average salary over the (final) three years prior to retirement.
DB Benefits Example
Example:
- A member with 40 years of service and salaries in the three years prior to retirement of $80,000, $85,000, and $75,000 would receive a pension of:
- A member with 15 years of service would receive:
Defined Benefit Fund Mechanics
- Trustees ensure the fund can pay defined benefits by requiring the employer or sponsor to contribute sufficient money.
- Contributions are determined by the fund actuary.
- Contributions and investment earnings must be sufficient to pay benefits under the Trust Deed.
- Benefits do not depend directly on the fund’s investment returns.
- Risk of low investment earnings is met by the employer, who may make higher contributions in such cases.
- In theory, benefits may be reduced, but this is unlikely to be allowed by the Trustees.
Defined Contribution Funds
Feature: Contribution is defined (by % of salary), retirement benefit depends on investment performance etc.
- The benefit payable on retirement is not defined.
- Determined by the amount that the contributions accumulate to, allowing for investment earnings, less charges for administration costs and the cost of death and disability cover.
- Usually provides life insurance charged against contributions.
- Governments usually provide favorable taxation treatment for superannuation savings (tax deferral).
Taxation of Superannuation Funds in Australia
Example 10.5: How does the Australian government tax superannuation funds at present?
Solution:
- Contributions into superannuation funds are taxed at 15% as income of the fund.
- Individuals are taxed on contributions above a specified level as income.
- The investment income of the funds is taxed at 15%.
- Benefits are taxed when they are paid at a reduced rate, giving credit for the 15% tax already paid.
- Governments usually limit the amount of retirement benefits that receive favorable taxation treatment due to this favorable taxation treatment.
Health Care and Disability
Health Care and Disability
Example 10.7: How is health care financed in Australia?
- Public health care for hospital and medical treatment is available and partly paid for by a Medicare levy based on taxable income.
- Private hospital treatment and additional health benefits are available at full cost to individuals without private insurance.
- Health insurance is available for private hospital and other health benefits.
- Community rating is used for private health insurance in Australia, where everyone pays the same rate regardless of risk.
Long-Term Care and Disability Income Insurance
Long-Term Care:
- Insurance companies in some countries have introduced policies providing income benefits for home and nursing home care.
- These policies pay benefits based on the number of Activities of Daily Living (ADLs) that the individual is unable to perform.
Disability Income Insurance:
- During an individual’s working life, disability or sickness can lead to a substantial loss of income.
- Insurance companies sell disability income insurance to cover this risk.
- Typical policies pay up to 75% of an individual’s income if they are disabled and unable to perform any occupation.
Lifecycle Model
Lifecycle Framework
The central problem: How can I best spread the income from the economically productive part of my life over my whole life?
Think of a lifetime as being divided into three (economic) stages:
- Childhood/Young adulthood: the growing up and getting education stage; pre-economic period of dependence and skill acquisition
- Working life: the wage-earning stage; period of economic accumulation
- Retirement: withdrawing from active working life; period of decumulation
Simple Lifecycle Model
The Lifecycle of ‘You, Inc’.
Lifetime resource management decisions start with analyzing resources:
- Starts as a subsidiary of Parents, Inc.
- Merger opportunities: Marriage
- Acquiring new headquarters: Home purchase
- Key decisions: Education, career, investments
Consider the following:
- What you own: Assets
- What you owe: Liabilities
- What is your Net Worth? How does it change over time?
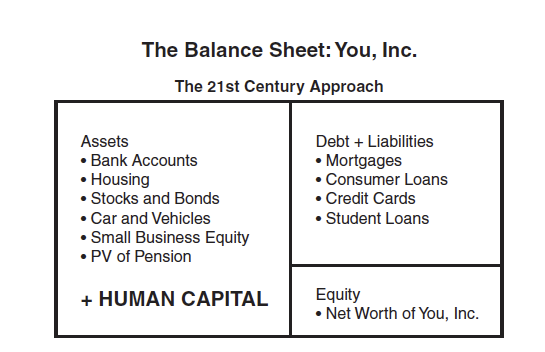
The Concept of Human Capital
- Human capital refers to your knowledge, skills, abilities, and social and personality attributes that enable you to generate labor income.
- Human capital can be measured through estimating the value of all your future earnings.
- Human Capital = Present value of expected future earnings.
- Where ( S ) is the expected salary
- ( g ) is the salary growth rate
- ( r ) is the interest rate
- ( n ) is the number of working years
Human Capital Example
Example:
- John graduates from university at age 22 and earns a starting salary of $50,000.
- John’s earnings grow by 3% per annum until retirement at age 65.
- Assume the interest rate of 3%.
- Ignoring taxes, what is the present value of his expected future earnings?
Calculation:
\[\text{PV} = 50,000 \sum_{i=1}^{43} \frac{(1.03)^{i-1}}{(1.03)^i} = \$2.09 \text{ million}\]